Operating Systems
What is a Mobile Operating System (OS)?
In layman’s terms, a mobile operating system (OS) is the central software that acts as the brain of your smartphone or tablet. It’s the invisible conductor that orchestrates everything happening behind the scenes, ensuring smooth communication between the device’s hardware (physical components) and software (apps and programs).
Think of it this way: Imagine your phone as a complex machine. The hardware is like the engine and gears, while the software is like the tools and instructions needed to operate it. The mobile OS acts as the intermediary, translating user commands (software) into actions the hardware can understand and execute.
Types of Mobile Operating Systems
This section dives into the two dominant mobile operating systems (OS): Android and iOS.
Android: The Open-Source Powerhouse
- History: Developed by Google and released in 2008, Android quickly gained popularity with its open-source nature. This allows manufacturers to customize the OS for their devices, leading to a diverse Android experience.
- Key Features:
- Customization: Extensive personalization options for themes, layouts, and functionalities.
- Openness: Wide variety of apps available beyond the official Google Play Store.
- Affordability: Android powers devices across various price points.
iOS: The Streamlined Experience
- History: Launched by Apple in 2007 alongside the first iPhone, iOS has been known for its tight integration with Apple hardware and software.
- Key Features:
- User-friendliness: Simple and intuitive interface designed for ease of use.
- Security: Renowned for its robust security features and frequent software updates.
- Performance: Optimized for seamless operation on Apple devices.
Choosing the Right OS for You:
The ideal mobile OS depends on your individual needs and preferences. Here are some key considerations:
- Customization: If you crave control over your device’s look and feel, Android might be the better choice.
- App Selection: If a vast app library is your priority, Android or iOS will likely have you covered.
- Integration: If you heavily rely on Apple products, iOS offers a seamless ecosystem. Windows Phone excels for those deeply invested in the Microsoft environment.
Beyond the Big Three:
While Android, iOS, and Windows Phone dominate the market, there are other niche players like BlackBerry OS and Sailfish OS catering to specific user groups.
-
Major Players: You’re right, Android and iOS are the most widely used mobile operating systems. They account for a vast majority of smartphones and tablets globally.
-
Other Options: There are other mobile OSes, though with a much smaller market share. Some examples include:
- KaiOS: This lightweight OS is popular in feature phones, known for its affordability and focus on essential functionalities.
- Sailfish OS: This open-source OS offers a unique user interface and focuses on security and privacy.
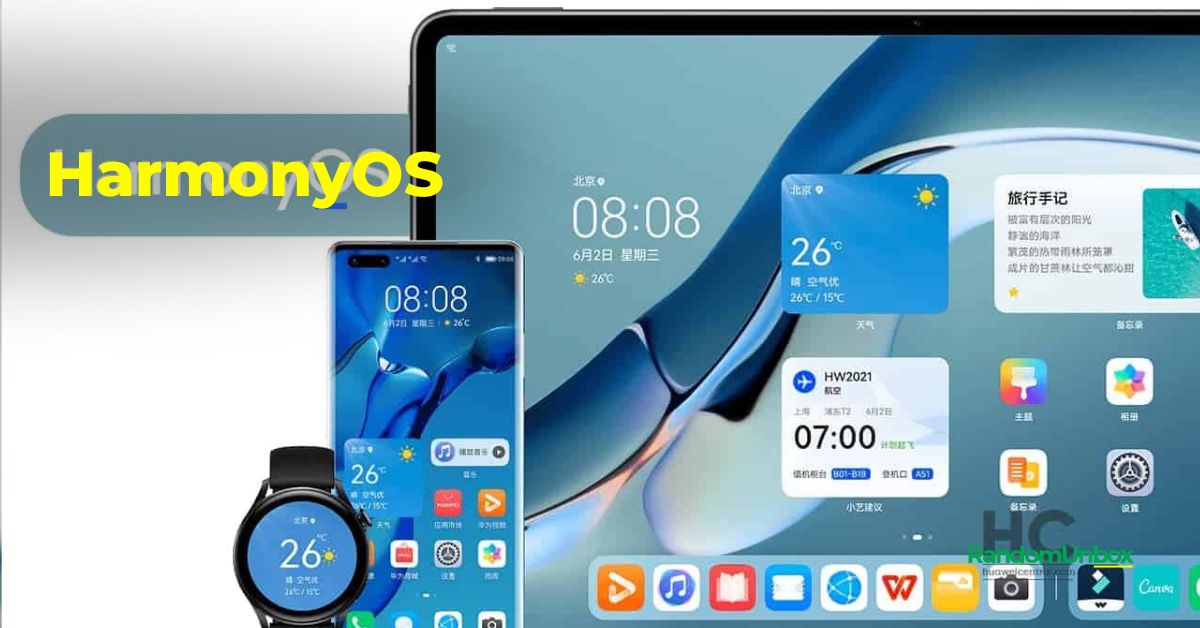
- HarmonyOS: Developed by Huawei, HarmonyOS is designed to work across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches.
- Plasma Mobile / postmarketOS: These are open-source projects aiming to bring a Linux-based mobile experience to different devices.
-
Discontinued Options: Some mobile OSes were once prominent but are no longer actively developed or supported. Examples include Windows Phone and BlackBerry OS.
While Android and iOS offer the widest app selection and user base, these alternative OSes cater to specific needs or preferences.
The Future of Mobile Operating Systems:
With constant innovation, the mobile OS landscape is ever-evolving. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and virtual reality could shape how we interact with these systems in the future.
Understanding the different types of mobile operating systems empowers you to make informed choices. Consider your priorities and explore what each OS has to offer to find the perfect fit for your mobile needs.
Core Functionalities of Mobile OS
A mobile operating system (OS) acts as the brain of your smartphone or tablet, controlling how you interact with the device and its hardware. Here’s a breakdown of its key functionalities:
A. User Interface (UI)
The UI is the graphical interface you use to interact with your device. It provides elements like the home screen, app drawer, and notifications that allow you to access apps, information, and perform actions. Some mobile OSes offer customization options to personalize the look and feel of your UI according to your preferences.
B. App Management
The mobile OS handles the installation, updates, and uninstallation of apps on your device. It ensures apps run smoothly and securely. Mobile app stores, like Google Play Store and Apple App Store, play a crucial role in discovering and distributing new apps. These stores curate and host apps, making them easily accessible to users through a secure platform.
C. Hardware Harmony
The OS acts as a bridge between you and your device’s hardware components like cameras, sensors, and memory. It manages how these components work together to deliver functionalities like taking pictures, using GPS navigation, and multitasking. The OS also handles memory management, allocating resources efficiently to ensure smooth operation, and power optimization to extend battery life.
D. Security
The mobile OS plays a vital role in safeguarding your device from security threats like malware and unauthorized access. It enforces security measures like permission control, which restricts apps from accessing sensitive data without your consent. Additionally, regular software updates from the OS provider address security vulnerabilities and keep your device protected.
Choosing a Mobile OS
Here are some key considerations to make when choosing a mobile OS:
- Budget: Do you prioritize high-end features or are you seeking a more affordable option?
- App Ecosystem: Does the platform offer the apps you use most frequently?
- Hardware Compatibility: Do you require specific features like a powerful processor or a high-quality camera?
- User Interface (UI) Preferences: Do you value ease of use or extensive customization options?
A Side-by-Side Look: Android vs iOS
The following table provides a quick comparison of key features between Android and iOS:
| Feature | Android | iOS |
|---|---|---|
| Openness (Customization) | More open platform, allowing for deeper customization | More restrictive platform, prioritizing a streamlined user experience |
| App Selection | Wider variety of apps available, including third-party options | Generally higher quality control over apps, with a focus on official releases |
| Hardware Integration | Works across a broader range of device manufacturers | Optimized for Apple devices (iPhones, iPads) |
Remember: There’s no single “best” mobile OS. The ideal choice depends on your specific needs and preferences.
Conclusion
In closing, this guide has explored the critical role mobile operating systems (OS) play in driving the functionality and user experience of our smartphones and tablets. We’ve delved into the key features and functionalities offered by various mobile OSes, highlighting their strengths and potential drawbacks.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Which mobile OS is more secure?
- Both Android and iOS offer robust security features. However, iOS tends to have a slight edge due to its closed ecosystem and stricter app review process.
-
Is Android better for multitasking?
- Yes, Android generally offers more advanced multitasking features like split-screen and floating windows.
-
Does iOS have more apps?
- Not necessarily. Both app stores offer a vast collection of apps, although the selection might differ slightly.
-
Is Android more customizable?
- Absolutely. Android allows for extensive customization with launchers, widgets, and themes.
-
Which OS receives faster updates?
- iOS devices typically receive software updates faster and for a longer duration compared to Android.
-
Is Android better for gamers?
- It depends on the game. Android offers more open hardware options for powerful gaming phones, but some high-end titles might launch first on iOS.
-
Is iOS more user-friendly?
- iOS is known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive design.
-
Does Android offer better battery life?
- Battery life varies depending on the specific device. Both OS have implemented battery optimization features.
-
Can I switch between Android and iOS?
- Yes, but it can be a complex process. Transferring data is easier when switching from Android to iOS.
-
Which mobile OS is right for me?
- The best choice depends on your individual needs and preferences. Consider factors like budget, desired level of customization, and app usage.